Ⅰ、 Dreileiter-PT100-Temperaturmessprinzip
Der Hauptzweck der Drei-Draht-Verbindungsmethode besteht darin, den Einfluss des Leitungswiderstands auf die Messgenauigkeit zu eliminieren. Der Widerstandswert des PT100 ist sehr klein (100Ω @ 0℃), und der Widerstand der Anschlussdrähte (einige Zehntel Ohm bis einige Ohm, geschrieben als R6, R7, R15, siehe Dreidraht-RTD-Prüfschema) kann nicht zu vernachlässigende Fehler verursachen. Das Dreileitersystem löst dieses Problem durch ein cleveres Schaltungsdesign, bei dem alle drei Leitungen eines Dreileiter-RTDs in der Regel gleich lang sind. Unter der Annahme, dass der Widerstand der drei Leitungen gleich ist (RL1 = RL2 = RL3, d.h. R6=R7=R15 im Schaltplan), wird die interne Doppelstromquelle (IDAC) des SSP1220 verwendet, um die Auswirkungen dieser Leitungswiderstände auszugleichen.
Ausführliche Erläuterung des Messprinzips:
- Bei Verwendung zweier passender programmierbarer Stromquellen (IDAC1 und IDAC2) innerhalb des SSP1220, die denselben Strom ausgeben, wird empfohlen, die Stromquelle mit weniger als 1 mA auszuwählen; der Auswahlwert für diesen Test beträgt 500uA.
- Es wird angenommen, dass die drei Leitungswiderstände des PT100 gleich sind: R6 = R7 = R15 = Rl
- Der SSP1220 misst die Spannung am PT100 über ein differentielles Eingangspaar (AIN0, AIN1): VIN = VAIN1 - VAIN0
in Erwägung nachstehender Gründe VAIN1 = IIDAC1 x (RL1+RPT100) + (IIDAC1 + IIDAC2) x RL3, VAIN0 = IIDAC2 x RL2 + (IIDAC1 + IIDAC2) x RL3
Seit: IIDAC1 = IIDAC2 = IIDAC UND RL1 = RL2 = RL3 = RL
zu ersetzen: VIN = [IIDAC x (RL + RPT100) + 2IIDAC x RL] - [IIDAC x RL + 2IIDAC x RL] = IIDAC x RL + IIDAC x RPT100 + 2IIDAC x RL - 2IIDAC x RL = IIDAC x RPT100
Durch eine geschickte Schaltungskonfiguration wird der Einfluss des Leitungswiderstandes vollständig aus der differentiellen Eingangsspannung VIN eliminiert, und nur der Spannungsabfall über dem PT100-Widerstand wird berücksichtigt.
- Die SSP1220-Referenzspannung Vref wird durch die Zusammenführung von zwei IDAC-Strömen über einen hochpräzisen externen Referenzwiderstand, Rref (R5), erzeugt, d.h. Vref = (Iidac1 + Iidac2) * R
- Bei Verhältnismessungen ist der endgültige ADC-Ausgangscode proportional zu (Rpt100) / (Rref), unabhängig vom Absolutwert, der Genauigkeit und der Drift des IDAC-Stroms, wobei auch die Wirkung der Leitungswiderstände Rl1 und Rl2 ausgeglichen wird:
Für den 24-Bit SSP1220 lautet der numerische Ausgangscode:
Code = (223 - 1) x (VIN/VREF) = (223 - 1) x [RPT100/(2 x RREF) ]
Invertierung des PT100-Widerstandswertes durch ADC-Code:
RPT100 = [Code/(223-1)] x 2 x RREF
Schließlich wird Rpt100 entsprechend der Widerstands-Temperatur-Charakteristik von PT100 (in der Regel unter Verwendung der Callendar-Van Dusen-Gleichung oder der Tabellen-Nachschlagemethode) in einen Temperaturwert umgerechnet: T = f (Rpt100). Für den PT100 beträgt der Widerstandstemperaturkoeffizient bei 0℃, R0 = 100,00Ω ungefähr α≈ 0,00385 Ω/Ω/℃.
Ⅱ、Hardware-Schaltungsentwurf
Gemäß der typischen Anwendung im Datenblatt sieht eine typische Dreileiter-PT100-Anschlussschaltung wie folgt aus:
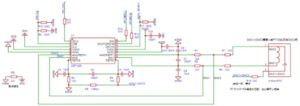
- Anweisungen zum Anschluss des Stromkreises
- PT100-Anschluss: Der PT100 (Dreileitersystem) wird wie im Schaltplan dargestellt angeschlossen.
- Erzeugung einer Spannungsreferenz: Der IDAC1-Ausgang ist mit AIN2 verbunden (interne Softwarekonfiguration erforderlich), der IDAC2-Ausgang ist mit AIN3 verbunden (interne Softwarekonfiguration erforderlich), und die beiden IDAC-Ströme laufen am Knoten zusammen und fließen gemeinsam durch den externen Referenzwiderstand Rref(R5). Das andere Ende von REF ist mit der analogen Masse AVSS verbunden. Der positive Referenzeingang des SSP1220, REFP0, ist mit dem oberen Ende von RREF (R5) (dem IDAC-Zusammenführungspunkt) verbunden. Der negative Referenzeingang des SSP1220, REFN0, ist mit AVSS verbunden. Daher ist die Referenzspannung, VREF= (IIDAC1 + IIDAC2) * RREF.
- Signalmessung: AIN1 für SSP1220 ist als positiver Differenzeingang AINP konfiguriert und AIN0 des SSP1220 ist als negativer Differenzeingang AINN konfiguriert, so dass die gemessene Spannung die Potentialdifferenz zwischen AIN1 und AIN0 ist.
- Filterung der Schaltung: RC-Tiefpassfilter müssen sowohl an den Analogeingängen (AIN0, AIN1, AIN2) als auch an den Referenzeingängen (REFP0) zur Antialiasing- und Rauschunterdrückung hinzugefügt werden. Eingangsfilter: bestehend aus R1, R2, C1 und C6, C5. Referenzfilter: Besteht aus R3, R4, C2 und C3, C4. Um die Genauigkeit der Skalenmessungen zu erhalten, sollte die Grenzfrequenz des Referenzfilters mit der des Eingangsfilters übereinstimmen.
Ⅲ、Geräteauswahl und Parameterberechnung
The hypothetical design objectives are as follows: PT100 type: three-wire; Temperature measurement range: -200°C ~ +850°C; Supply voltage AVDD: 3.3V (AVSS = 0V); DAC Current: 500μA (per channel); Data rate: 20 SPS (for optimal noise performance).
- Reference resistance (Rref) selection and calculation
Rref is at the heart of the accuracy of the entire system. Function: Generate the reference voltage V ref of the ADC, and its accuracy and stability directly determine the measurement results.
Resistance Calculation:
To maximize the range of the ADC and meet the common mode voltage requirements of the PGA, the Vref is typically set at about half the supply voltage. In this design, AVDD = 3.3V and the target VREF is about 1.65V.
IIDAC = I_IDAC1 + I_IDAC2 = 500uA + 500uA = 1mA
RREF = VREF /(IIDAC1 + IIDAC2) = 1.65V/1mA = 1.65kΩ
A resistor with a nominal value of 1.65 kΩ can be selected. If not found, 1.62kΩ or 1.69kΩ is also an acceptable approximation.
Selection requirements:
Accuracy: At least ±0.1%, recommended ±0.05% or higher for high-precision applications.
Temperature Bleating: Must be very low, with precision film resistance of ±5 ppm/°C or ±10 ppm/°C recommended.
Long-term stability: high.
Never use a normal 1%, 100ppm/°C chip resistor.
- IDAC current and PGA gain options
IDAC Current: 500μA selected. This value strikes a good balance between power consumption, self-heating effect, and signal amplitude. If the current is too small, the signal is weak and easily affected by noise; Too much current may cause the PT100 to self-heat or exceed IDAC compliant voltages.
PGA Gain Selection: The PT100 has a smaller voltage (e.g. 500μA × 100Ω = 50mV), but uses a ratio measurement (the reference voltage is also from IDAC), so there is no need to amplify to avoid saturation, and the gain selection is 1X.
- Filter circuit component selection
Filter Resistors (R1, R2, R3, R4): 1kΩ is usually selected. This value is large enough to effectively filter and small enough to avoid significant offset voltages at the input (due to input bias current). They also act as current-limiting protection.
Differential filter capacitors (C1, C2): Set the cut-off frequency together with the resistor. For example, for a data rate of 20SPS, the cut-off frequency can be set in the tens of Hz. fc = 1 / (2π * (R1+R2) * C1)。 If R1+R2=2kΩ and expects fc ≈ 16Hz, C1 ≈ 1 / (2* 2000 * 16) ≈ 4.7μF. In real-world applications, 100nF (0.1μF) is often used to obtain a wider noise rejection bandwidth. Type: C0G (NPO) ceramic capacitors are recommended for their stable dielectric constant, low voltage coefficient, and low microacoustic effect.
Common-mode filtered capacitors (C5, C6, C3, C4): Typically chosen an order of magnitude smaller than differential capacitors, such as 10nF, to ensure that mismatches of differential capacitors do not result in excessive common-mode noise being converted into differential noise.
Ⅳ、Software configuration
- Master Logic:
float SSP1x20_read_temperature(void)
{
uint32_t ADC_data;
uint32_t ADC_temp1;
//SSP1x20_read_register(SSP1x20_REG0, 4, &Read_REGTab[0]);
Write_REGTab[0] = SSP1x20_MUX_AIN0_AIN1 | SSP1x20_GAIN_1 | SSP1x20_PGA_BYPASS_ON;
Write_REGTab[1]=SSP1x20_DR_20SPS|SSP1x20_MODE_NORMAL|SSP1x20_SC|SSP1x20_TS_ON| SSP1x20_BCS_OFF;
Write_REGTab[2]=SSP1x20_VREF_2048|SSP1x20_REJECT_OFF|SSP1x20_PSW_OFF | SSP1x20_IDAC_1000uA;
Write_REGTab[3] = SSP1x20_IDAC1_AIN2 | SSP1x20_IDAC2_AIN3 | SSP1x20_DRDYM_DRDY;
SSP1x20_WriteRegister(SSP1x20_REG0, 4, &Write_REGTab[0]);
SSP1x20_SendCommand(SSP1x20_CMD_START);
SPI_ADC_CS_LOW();
while (ADC_DRDY_GAIN == 1);//SSP1x20_DRDYM_DRDY
- The main configuration and description of the program
- Configure register 0: MUX and gain
Write_REGTab[0] = SSP1x20_MUX_AIN0_AIN1 | SSP1x20_GAIN_1 | SSP1x20_PGA_BYPASS_ON;
| Bit | Configuration | Function | Beschreibung |
| BIT7~BIT4 | MUX_AIN0_AIN1 | Differential input channel selection | AIN0 – AIN1 → for PT100 voltage measurement |
| BIT3~BIT1 | GAIN_1(1x gain ) | Gain settings | 1× (no need to amplify as Vin ≈ 1V) |
| BIT0 | PGA_BYPASS_ON | PGA bypass | Schalten Sie den programmierbaren Verstärker aus, um Signalverzerrungen zu vermeiden. |
- Konfigurationsregister 1: Abtastrate und Modus
Write_REGTab[1] = SSP1x20_DR_20SPS | SSP1x20_MODE_NORMAL | SSP1x20_SC | SSP1x20_TS_OFF | SSP1x20_BCS_OFF;
| Bit | Configuration | Function | Beschreibung |
| BIT7~BIT5 | DR_20SPS | Datenrate | 20 mal/sec → geeignet für langsame Temperaturänderungen |
| BIT4~BIT3 | MODUS_NORMAL | Normaler Arbeitsmodus | Nicht einzeln oder fortlaufend |
| BITO | SC | Selbstkalibrierung aktiviert | Verbesserte Genauigkeit (empfohlen) |
| BIT1 | TS_OFF | Deaktivieren Sie den internen Temperatursensor | TS_ON schaltet den internen Temperatursensor ein, die Konfiguration zur Messung der externen Temperatur funktioniert nicht (diese Konfiguration hat die höchste Priorität) |
- Register 2 konfigurieren: Referenzspannung mit IDAC
Write_REGTab[2] = SSP1x20_VREF_2048 | SSP1x20_REJECT_OFF | SSP1x20_PSW_OFF | SSP1x20_IDAC_500uA;
| Bit | Configuration | Function | Beschreibung |
| BIT7~BIT6 | VREF_2048 | Externe Referenzspannung | Verwenden Sie einen externen R_REFR_REF, um eine Referenzspannung zu erzeugen (z. B. 1,65kΩ). |
| BIT5~BIT4 | REJECT_OFF | Keine Kerbfilterung | Es ist keine Störfestigkeit gegen Netzfrequenzstörungen erforderlich. |
| BIT3 | PSW_OFF | Aktivieren Sie den Netzschalter nicht | Aufrechterhaltung der normalen Stromversorgung |
| BIT2~BIT0 | IDAC_500uA | Erregerstrom | Auf 500 μA einstellen, um eine Überspannung von 3,9kΩ × 1mA = 3,9V > 3,3V zu vermeiden |
| Bit | Configuration | Function | Beschreibung |
| BIT7~BIT5 | IDAC1_AIN2 | IDAC1-Ausgang an AIN2 | Der Erregerstrom fließt durch das obere Ende des PT100 |
| BIT4~BIT2 | IDAC2_AIN3 | IDAC2-Ausgang an AIN3 | Rückkehr in den Pfad, um den Leitungswiderstand auszugleichen |
| BIT1 | DRDYM_DRDY | DRDY-Modus | Verwenden Sie das DRDY-Signal, um Ihnen mitzuteilen, dass die Konvertierung abgeschlossen ist. |
(4) Register 3 konfigurieren: IDAC-Routenkanal mit DRDY
- Dreidraht-PT100-Kern:
Aktueller Pfad:
- IDAC1 → AIN2 → PT100 → AIN1
- IDAC2 → AIN3 → AIN1(Rückgabe)
- Two currents are equal → offset the voltage drop on the R_LEAD2R_LEAD2
uint32_t raw_u24 = SSP1x20_read_data_drdy();
SSP1220 outputs 24-bit data, but MCUs typically read in 32-bit (SPI reads 4 bytes at a time).
if (raw < 0) raw = -raw;
The PT100 voltage is always positive (current flows from AIN0 to AIN1).
If raw < 0, the AIN0 and AIN1 software configurations are reversed.
printf(“Raw: %ld, R=%.3f Ω, Temp=%.2f °C\r\n”, raw, R_pt100, temperature);
Print the original code value, calculate the resistance, and the final temperature for easy debugging
If Raw is negative→ the configuration is reversed
If R > 1400Ω → indicates that the IDAC or Rref is set incorrectly
If Temp = -999 → indicates that the R-value is outside the reasonable range
Ⅴ、Measurement procedure and results
- PT100 voltage measurement program at both ends:
void SSP1x20_ADC_MeasurePt100(void)
{
float V_ref = 2.048; // Internal reference voltage 2.048V
//printf(“\r\n Multi-point single voltage measurement \r\n”);
Write_REGTab[0] = SSP1x20_MUX_AIN1_AIN0 | SSP1x20_GAIN_1 | SSP1x20_PGA_BYPASS_OFF;
Write_REGTab[1] = SSP1x20_DR_20SPS | SSP1x20_MODE_NORMAL | SSP1x20_SC | SSP1x20_TS_OFF | SSP1x20_BCS_OFF;
Write_REGTab[2] = SSP1x20_VREF_REF0 | SSP1x20_REJECT_OFF | SSP1x20_PSW_OFF | SSP1x20_IDAC_500uA;
Write_REGTab[3] = SSP1x20_IDAC1_AIN2 | SSP1x20_IDAC2_AIN3 | SSP1x20_DRDYM_DRDY;
SSP1x20_WriteRegister(SSP1x20_REG0, 4, &Write_REGTab[0]);
printf(“Write_REGTab[0]=%x\r\n”, Write_REGTab[0]);
printf(“Write_REGTab[1]=%x\r\n”, Write_REGTab[1]);
printf(“Write_REGTab[2]=%x\r\n”, Write_REGTab[2]);
printf(“Write_REGTab[3]=%x\r\n”, Write_REGTab[3]);
while (1)
{
SSP1x20_SendCommand(SSP1x20_CMD_START); // When continuous measurement is enabled, this command is sent only once
HAL_Delay(100);
SPI_ADC_CS_LOW();
}
SSP1220 test results
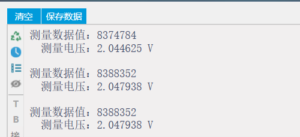
- SSP1220 internal temperature measurement
Internal temperature test function
float SSP1x20_read_temperature(void)
{
uint32_t ADC_data;
uint32_t ADC_temp1;
//SSP1x20_read_register(SSP1x20_REG0, 4, &Read_REGTab[0]);
Write_REGTab[0] = SSP1x20_MUX_AIN0_AIN1 | SSP1x20_GAIN_1 | SSP1x20_PGA_BYPASS_ON;
Write_REGTab[1] = SSP1x20_DR_20SPS | SSP1x20_MODE_NORMAL | SSP1x20_SC | SSP1x20_TS_ON | SSP1x20_BCS_OFF;
Write_REGTab[2] = SSP1x20_VREF_2048 | SSP1x20_REJECT_OFF | SSP1x20_PSW_OFF | SSP1x20_IDAC_1000uA;
Write_REGTab[3] = SSP1x20_IDAC1_AIN2 | SSP1x20_IDAC2_AIN3 | SSP1x20_DRDYM_DRDY;
SSP1x20_WriteRegister(SSP1x20_REG0, 4, &Write_REGTab[0]);
SSP1x20_SendCommand(SSP1x20_CMD_START);
SPI_ADC_CS_LOW();
while (ADC_DRDY_GAIN == 1);//SSP1x20_DRDYM_DRDY
Internal temperature test configuration details:
Write_REGTab[1] = SSP1x20_DR_20SPS | SSP1x20_MODE_NORMAL | SSP1x20_SC | SSP1x20_TS_ON | SSP1x20_BCS_OFF;
- SSP1x20_TS_ON: Enable the internal temperature sensor (critical), this configuration has the highest priority
- SSP1x20_SC: Perform self-calibration (recommended)
- 20SPS: Low speed and high accuracy, suitable for temperature measurement
Write_REGTab[2] = SSP1x20_VREF_2048 | SSP1x20_REJECT_OFF | SSP1x20_PSW_OFF | SSP1x20_IDAC_1000uA;
- SSP1x20_VREF_2048: Use an internal 2.048V reference voltage (not external REF0!) )
- Because the internal temperature sensor is an absolute voltage output, a fixed reference voltage must be used to convert the temperature.
- IDAC_1000uA: Although IDAC is enabled, IDAC in TS_ON mode does not affect internal temperature measurements (negligible).
Write_REGTab[3] = SSP1x20_IDAC1_AIN2 | SSP1x20_IDAC2_AIN3 | SSP1x20_DRDYM_DRDY;
- Configure the IDAC pin and DRDY, but have no effect on the internal temperature measurement (just keep the registers intact).
- 2 Start the conversion and wait for DRDY
SSP1x20_SendCommand(SSP1x20_CMD_START); SPI_ADC_CS_LOW();while (ADC_DRDY_GAIN == 1); // 等待 DRDY 变低
- Send the START command to start a continuous transition
- Wait for the DRDY pin to go low, indicating that the data is ready
The measurement of indoor room temperature is shown in the figure below:
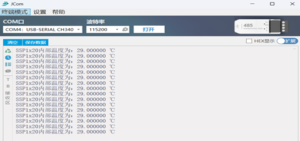
3. External temperature measurement (method 1, simplified factor 0.385 calculation)
External temperature test related code:
uint32_t ADC_gain_value = 0; // Readout data
uint32_t ADC_value = 0; // Measure the data value
float tmpPt100=0;
float RTD=0;
void SSP1x20_ADC_Measure(void)
{
printf(“\r\n Multi-point single voltage measurement \r\n”);
Write_REGTab[0] = SSP1x20_MUX_AIN1_AIN0 | SSP1x20_GAIN_1 | SSP1x20_PGA_BYPASS_OFF; SSP1x20_MUX_AIN1_AIN0 Interface AIN1 AIN0 should be selected based on the actual circuit diagram
Write_REGTab[1] = SSP1x20_DR_20SPS | SSP1x20_MODE_NORMAL | SSP1x20_SC | SSP1x20_TS_OFF | SSP1x20_BCS_OFF;
Write_REGTab[2] = SSP1x20_VREF_REF0 | SSP1x20_REJECT_OFF | SSP1x20_PSW_OFF | SSP1x20_IDAC_500uA;
Write_REGTab[3] = SSP1x20_IDAC1_AIN2 | SSP1x20_IDAC2_AIN3 | SSP1x20_DRDYM_DRDY;
SSP1x20_WriteRegister(SSP1x20_REG0, 4, &Write_REGTab[0]);
printf(“Write_REGTab[0]=%x\r\n”, Write_REGTab[0]);
printf(“Write_REGTab[1]=%x\r\n”, Write_REGTab[1]);
printf(“Write_REGTab[2]=%x\r\n”, Write_REGTab[2]);
printf(“Write_REGTab[3]=%x\r\n”, Write_REGTab[3]);
while (1)
{
SSP1x20_SendCommand(SSP1x20_CMD_START); When continuous measurement is enabled, this command is sent only once
HAL_Delay(100);
SPI_ADC_CS_LOW();
ADC_gain_value =0;
ADC_gain_value = SPI_ADC_ReadByte();
ADC_gain_value = (ADC_gain_value << 8) | SPI_ADC_ReadByte();
ADC_gain_value = (ADC_gain_value << 8) | SPI_ADC_ReadByte();
SPI_ADC_CS_HIGH();
RTD = 1650*( (float)ADC_gain_value /(0x3fffff));//Reference resistance 1650 ohms
tmpPt100 = (RTD-100)/0.38;
__NOP();
printf(“R=%.3f Ω, Temp=%.2f °C\r\n”,RTD, tmpPt100 );
}
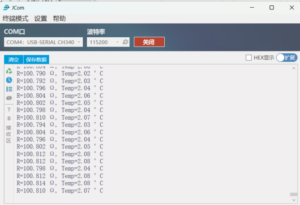
The results of the three-line RTD measurement of the temperature of the ice water mixture are shown in the figure below:

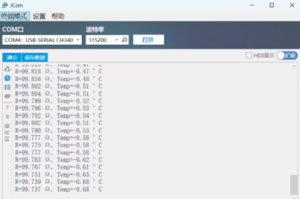
External temperature measurements (method two, calculated by the Callendar-Van Dusen equation) are more accurate
Master Code:
//High accuracy RTD -> temperature
static float rtd_to_temperature_iec60751(float rtd)
{
if (rtd < 0.0f) return -999.0f; // illegal value
float t = (rtd – R0_PT100) / 0.385f; // initial guess
if (rtd <= R0_PT100) {
//T < = 0°C: Use the complete equation
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
float rt_calc = R0_PT100 * (1.0f + A_COEFF*t + B_COEFF*t*t + C_COEFF*(t – 100.0f)*t*t*t);
float dr_dt = R0_PT100 * (A_COEFF + 2.0f*B_COEFF*t + C_COEFF*(4.0f*t*t*t – 300.0f*t*t));
float error = rt_calc – rtd;
t -= error / dr_dt;
if (fabsf(error) < 0.001f) break;
}
} else {
// T >= 0°C:: Use the simplified equation
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
float rt_calc = R0_PT100 * (1.0f + A_COEFF*t + B_COEFF*t*t);
float dr_dt = R0_PT100 * (A_COEFF + 2.0f*B_COEFF*t);
float error = rt_calc – rtd;
t -= error / dr_dt;
if (fabsf(error) < 0.001f) break;
}
}
return t;
}
/**
* @brief Analog channel ADC measurement (external temperature measurement)
* @param None
* @retval None
*/
uint32_t ADC_gain_value = 0; // Readout data
uint32_t ADC_value = 0; // Measure the data value
float tmpPt100=0;
float RTD=0;
void SSP1x20_ADC_Measure(void)
{
printf(“\r\n Multi-point single voltage measurement \r\n”);
Write_REGTab[0] = SSP1x20_MUX_AIN1_AIN0 | SSP1x20_GAIN_1 | SSP1x20_PGA_BYPASS_OFF;
Write_REGTab[1] = SSP1x20_DR_20SPS | SSP1x20_MODE_NORMAL | SSP1x20_SC | SSP1x20_TS_OFF | SSP1x20_BCS_OFF;
Write_REGTab[2] = SSP1x20_VREF_REF0 | SSP1x20_REJECT_OFF | SSP1x20_PSW_OFF | SSP1x20_IDAC_500uA;
Write_REGTab[3] = SSP1x20_IDAC1_AIN2 | SSP1x20_IDAC2_AIN3 | SSP1x20_DRDYM_DRDY;
// Write_REGTab[3] = SSP1x20_IDAC1_AIN3 | SSP1x20_IDAC2_AIN2 | SSP1x20_DRDYM_DRDY;
SSP1x20_WriteRegister(SSP1x20_REG0, 4, &Write_REGTab[0]);
printf(“Write_REGTab[0]=%x\r\n”, Write_REGTab[0]);
printf(“Write_REGTab[1]=%x\r\n”, Write_REGTab[1]);
printf(“Write_REGTab[2]=%x\r\n”, Write_REGTab[2]);
printf(“Write_REGTab[3]=%x\r\n”, Write_REGTab[3]);
while (1)
{
SSP1x20_SendCommand(SSP1x20_CMD_START); When continuous measurement is enabled, this command is sent only once
HAL_Delay(100);
SPI_ADC_CS_LOW();
ADC_gain_value =0;
ADC_gain_value = SPI_ADC_ReadByte();
ADC_gain_value = (ADC_gain_value << 8) | SPI_ADC_ReadByte();
ADC_gain_value = (ADC_gain_value << 8) | SPI_ADC_ReadByte();
SPI_ADC_CS_HIGH();
#define CALIBRATED_FULL_SCALE 4210300.0f // ccording to calibration data
RTD = 1650.0f * ((float)ADC_gain_value / CALIBRATED_FULL_SCALE);
tmpPt100 = rtd_to_temperature_iec60751(RTD);
__NOP();
printf(“R=%.3f Ω, Temp=%.2f °C\r\n”,RTD, tmpPt100 );
}
}
The test results are shown in the figure:
Hot Water Temperature Test:
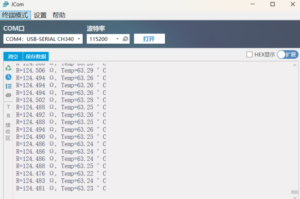

Ice Water Mixture Test:

4. External temperature test configuration details:
| Register | Configure values (your code) | Function description: | Why did you choose this? |
| REG0 Write_REGTab[0] | SSP1x20_MUX_AIN1_AIN0 | SSP1x20_GAIN_1 |SSP1x20_PGA_BYPASS_OFF | Enter Channel Selection + Gain Settings | |
| SSP1x20_MUX_AIN1_AIN0 | Differential inputs: AIN1 is positive and AIN0 is negative | The PT100 is connected to AIN0 and AIN1 on both ends and requires differential voltage measurement. ⚠️ Note the polarity: if the configuration is reversed, the ADC outputs a negative value (e.g., 0x800000), resulting in a negative temperature. | |
| SSP1x20_GAIN_1 | Gain = 1 | The PT100 has a smaller voltage (e.g. 500μA × 100Ω = 50mV), but uses a ratio measurement (the reference voltage is also from IDAC), so no amplification is required to avoid saturation. | |
| SSP1x20_PGA_BYPASS_OFF | No bypass PGA | Keep the PGA function (even if the gain=1) to ensure the signal path is normal. | |
| REG1 Write_REGTab[1] | SSP1x20_DR_20SPS | SSP1x20_MODE_NORMAL | SSP1x20_SC | SSP1x20_TS_OFF | SSP1x20_BCS_OFF | Data rate + operating mode | |
| SSP1x20_DR_20SPS | Sample rate = 20 sample points/second | Low speed improves accuracy, suppresses noise, and is suitable for temperature measurement (slow change). | |
| SSP1x20_MODE_NORMAL | Normal continuous conversion mode | Continuous data output for real-time monitoring. | |
| SSP1x20_SC | Perform self-calibration | Calibration after each configuration, eliminates offset/gain errors and improves accuracy. | |
| SSP1x20_TS_OFF | Turn off the internal temperature sensor | We measure the external PT100 and do not need the internal temperature. | |
| SSP1x20_BCS_OFF | Disable burn-off current sources | No, you don’t. | |
| REG2 Write_REGTab[2] | SSP1x20_VREF_REF0 | SSP1x20_REJECT_OFF | SSP1x20_PSW_OFF SSP1x20_IDAC_500uA | Reference Voltage + IDAC Settings | |
| SSP1x20_VREF_REF0 | Use an external reference voltage (REF0 = voltage between AIN2/AIN3). | Implement ratio-based measurements: ADC result = (Vpt100 / Vref) × 224, independent of IDAC current absolute, only related to Rref, resistant to power supply fluctuations. | |
| SSP1x20_REJECT_OFF | 50/60Hz suppression is not enabled | If the environmental interference is small, it can be turned off; If it is in a power frequency environment, it is recommended to turn on the REJECT_50. | |
| SSP1x20_PSW_OFF | Turn off the sensor power supply switch | The PT100 is powered by IDAC and does not require additional PSW. | |
| SSP1x20_IDAC_500uA | Set constant current source current = 500 μA | Common current values, balancing power consumption and signal amplitude (100Ω → 50mV). | |
| REG3 Write_REGTab[3] | SSP1x20_IDAC1_AIN2 | SSP1x20_IDAC2_AIN3 | SSP1x20_DRDYM_DRDY | IDAC output pin + DRDY configuration | |
| SSP1x20_IDAC1_AIN2 | IDAC1 output to AIN2 | AIN2 to PT100 (excitation) | |
| SSP1x20_IDAC2_AIN3 | IDAC2-Ausgang an AIN3 | AIN3 is connected to the reference resistor at one end of the R_ref (forming the loop) → realizes three-wire compensation (offsetting the wire resistance). | |
| SSP1x20_DRDYM_DRDY | Enable the DRDY pin (Data Ready Signal). | The MCU detects DRDY low levels through GPIO to know when data is being read and avoid polling. |
——————————————————————————————————
Key Part Code Formula Calculation:
RTD = 1650*( (float)ADC_gain_value /(0x3fffff)); //reference resistance 1650 ohms tmpPt100 = (RTD-100)/0.385;
Reference resistance 1650 ohms,
First line code RTD = 1650 * (ADC / 0x3FFFFF)
Designed to convert the original ADC value to the resistance value of the PT100 (ratio measurement)
- VIN = I × RPT100 (voltage across PT100)
- VREF = I × RREF (voltage across reference resistor)
The same constant current source I adc is used at both ends
So: Vin/Vref = Rpt100/Rref
The output of the ADC is the digitized result of this ratio
ADC_Code = Vin/Vref x 224
So pushed back
Rpt100= Rref x ADC_Code /224
———————————————————————————————————————
Second line code: tmpPt100 = (RTD – 100) / 0.385;
Estimate the temperature with a linear approximation formula
At 0°C, Rpt100 = 100 Ω
For every 1°C increase in temperature, the resistance increases by about 0.385 Ω
So
T ≈ (R-100)/0.385
Ⅵ、 Common Problem Debugging Guide
| Anomal | Possible causes | Troubleshooting steps |
| The original value of the ADC (raw) is negative | AIN0 is the opposite of AIN1 configuration | 1. Check that the software configuration is consistent with the connection to the hardware |
| R_PT100 > 1400Ω | 1. Incorrect IDAC current configuration; 2. Rref opens | 1. Check the IDAC configuration of REG2 (make sure it is 500μA); 2. Measure the R ref resistance value with a multimeter to confirm that the circuit is not open |
| The temperature value is – 999°C | PT100 exceeds the 18Ω~330Ω range | 1. Check if the PT100 is disconnected (measure the PT100 resistance); 2. Verify SPI Communication (Read Register Configuration Values) |
| Temperature fluctuations > 0.1°C | 1. Large ripple of power supply; 2. Electromagnetic interference | 1. SSP1220 VDD-Welligkeit messen (≤ 10mV erforderlich); 2. Prüfen Sie die Erdung des Abschirmdrahtes, um Störungen zu vermeiden. |
Ⅶ、 SSP1220 Core Register Konfigurationstabelle
| Register | Artikel konfigurieren | Wert (externe Temperaturmessung) | Function description: |
| REG0 | Differenzielle Kanäle | AIN1-AIN0 | Passen Sie die PT100-Verdrahtung an, um negative Rohdaten zu vermeiden. |
| gewinnen | 1× | Vermeidung von Signalsättigung und Anpassung an die Verhältnismessung | |
| PGA bypass | deaktivieren | Bewahrung der Integrität des Signalwegs | |
| REG1 | Abtastrate | 20SPS | Niedrige Geschwindigkeit verbessert die Genauigkeit und passt sich an langsame Temperatursignale an |
| Arbeitsmodus | Normaler Modus | Kontinuierliche Umwandlung und Echtzeitausgabe von Temperaturdaten | |
| Selbstkalibrierung | aktivieren. | Beseitigung von Offset-/Gain-Fehlern und Verbesserung der Genauigkeit | |
| Interner TS | deaktivieren | Externe Temperaturmessung erfordert keine internen Sensoren | |
| REG2 | Referenzspannung | Externer REF0 | Ratio-basierte Messung zum Ausgleich von IDAC-Stromschwankungen |
| IDAC-Strom | 500μA | Symmetrische Leistungsaufnahme und Signalamplitude (50mV 100Ω) | |
| REG3 | IDAC1-Routen | AIN2 | Der Erregerstromeingang PT100 |
| IDAC2-Routen | AIN3 | Dem Vorwiderstand R7 entgegenwirken |
Tabelle der Koeffizienten der Ⅷ、Callendar-Van Dusen-Gleichung
| Koeffizient | Numerischer Wert | Einheit | Umfang der Anwendung |
| R0 | 100.0 | Ω | 0°C Bezugswiderstand |
| A | 3.9083×10-3 | ℃-1 | -200℃~600℃ |
| B | -5.775×10-7 | ℃-2 | -200℃~600℃ |
| C | -4.183×10-12 | ℃-4 | -200℃~0℃ |
Den vollständigen Code erhalten Sie, wenn Sie sich an unseren technischen Support wenden. Kontakt: 18014203727
_画板-1@2x.png)