Application
Search
Post Catgories
Have Any Queries?
Click the button to leave your message and we’ll get back to you as soon as possible.
In modern industrial measurement and automation control, resistive bridge sensors are widely used in the detection of physical quantities such as weight, pressure, and strain due to their high accuracy and stability. However, how to design a high-performance resistance bridge measurement system and ensure its reliability and accuracy in practical applications is a challenge faced by many engineers and technicians.
SSP1220 three-wire RTD measurement

In today's rapid development of the Internet of Things and intelligent hardware, efficient and reliable motor drive technology has become the core requirement of robots, smart toys and consumer electronics. The SSP2617 single-channel H-bridge driver chip launched by Shanghai Siproin Microelectronics is redefining the performance standard of low-voltage motion control scenarios with its excellent power handling capabilities, flexible PWM control, and multiple protection mechanisms.

Today, let's talk about two very important concepts in switching power supplies -- synchronous rectification and asynchronous rectification. The switching power supply relies on the inductive charging energy storage when the power tube is opened, and the inductive energy is released when the power tube is disconnected to realize the voltage transformation. After the power tube is disconnected, the inductance releases energy to have a current loop, which is different in the selection of current components, it will involve different rectification methods, that is, synchronous rectification and asynchronous rectification. So what is the difference between them?

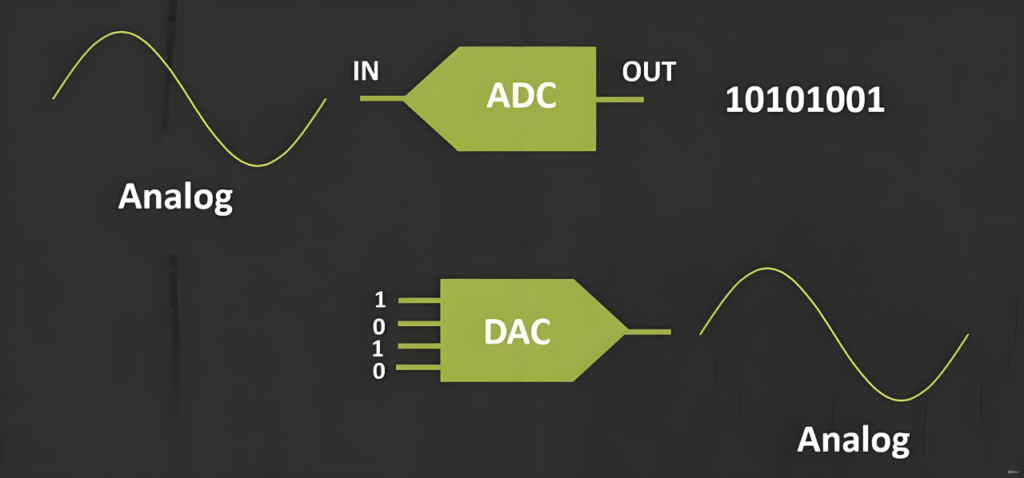
Ultrasonic heat meters are instruments that measure flow rates and display the thermal energy released or absorbed by water passing through a heat exchange system using ultrasonic methods. The device calculates the heat energy by measuring two physical quantities—the flow rate of the heat carrier and the temperature difference between the inlet and outlet—then applies compensation for density and enthalpy values and performs integration. Specifically, the ultrasonic time-difference method relies on the time difference of ultrasonic signals propagating in the fluid to measure flow rates.

Input voltage (withstand voltage): it refers to the voltage range of 78L33 Vin. If the input voltage is higher than the maximum working voltage of 78L33, it will exceed the voltage withstand degree and damage. If the input voltage is lower than the minimum working voltage of 78L33, then 78L33 will not work properly.
_画板-1@2x.png)
